Water hardness is an important parameter in various industries, including water treatment, pharmaceuticals, and laboratories. To measure hardness, two popular methods are commonly used: EDTA titration and hardness meters. But which one is more accurate? Many professionals debate whether EDTA titration is more accurate than a hardness meter, and the answer depends on various factors, such as precision, ease of use, and cost. In this article, we will explore both methods in detail, compare their accuracy, and help you decide which method is better suited for your needs.
What Is EDTA Titration and How Does It Work?
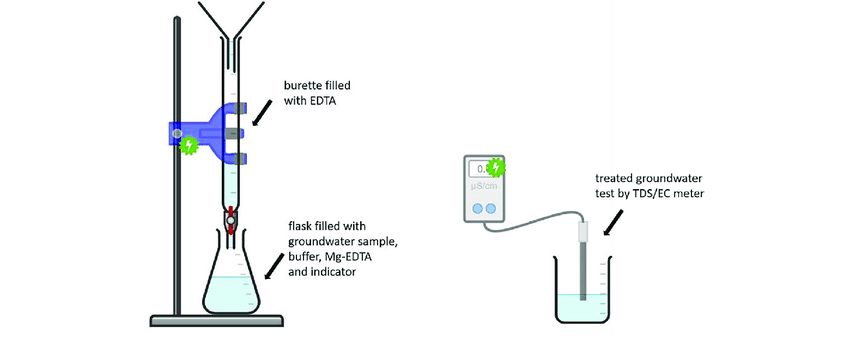
EDTA titration is a chemical method used to determine water hardness by measuring the concentration of calcium (Ca²⁺) and magnesium (Mg²⁺) ions. The process involves adding a specific amount of EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) solution to a water sample. EDTA binds with the hardness ions, forming a stable complex. A color indicator, such as Eriochrome Black T, is used to signal the endpoint of the reaction when all hardness ions have reacted with EDTA.
The titration process follows these steps:
- A water sample is collected, and a buffer solution is added to maintain the pH.
- An indicator is introduced, changing color when all hardness ions are complexed.
- EDTA is slowly added from a burette, reacting with calcium and magnesium ions.
- The endpoint is reached when the solution changes color, indicating all hardness ions are complexed.
- The volume of EDTA used is recorded, and the hardness concentration is calculated.
EDTA titration is widely used in laboratories because it provides reliable and repeatable results. However, it requires skilled personnel to perform accurately.
What Is a Hardness Meter?
A hardness meter is a digital device that quickly measures water hardness using sensors or probes. These meters detect electrical conductivity changes in the water sample, which correlate to calcium and magnesium ion concentrations.
There are two main types of hardness meters:
- Electronic hardness meters – Use electrical conductivity to estimate hardness levels.
- Colorimetric test kits – Use reagents to produce a color change, which is then compared to a reference chart.
Hardness meters are widely used in industries such as boiler maintenance, food processing, and water treatment plants, where quick and on-site hardness testing is required.
EDTA Titration vs. Hardness Meter – Which One is Better?
Both EDTA titration and hardness meters have advantages and disadvantages. To determine which method is better, we need to compare them based on accuracy, ease of use, and cost.

Accuracy – Which Method Gives the Best Results?
When it comes to accuracy, EDTA titration generally provides more precise results compared to hardness meters. The reasons for this include:
- Higher Sensitivity: EDTA titration detects even small variations in hardness levels.
- Elimination of Interferences: Digital meters can be affected by temperature, dissolved salts, and electrical interference, leading to less accurate readings.
- More Reliable for Low Hardness Levels: Hardness meters struggle to measure very low concentrations accurately.
While digital hardness meters offer convenience, they can sometimes give inconsistent results due to calibration errors or sensor degradation. For laboratory and high-precision applications, EDTA titration is the preferred method.
Ease of Use – Which Method is Simpler?
If simplicity and speed are priorities, hardness meters are the better choice.
- Hardness meters provide results within seconds by simply dipping the probe into the water sample.
- Minimal training is required, making them suitable for field testing.
- No chemical handling is needed, reducing safety concerns.
On the other hand, EDTA titration requires lab skills and a controlled environment to ensure accurate measurements. It involves multiple steps, including reagent preparation, buffering, and endpoint detection. This makes it more time-consuming and prone to human errors if not done correctly.
Cost – Which Method is More Affordable?
The cost comparison between EDTA titration and hardness meters depends on usage:
- EDTA titration is cheaper for laboratories since reagents and glassware are relatively inexpensive. However, it requires trained personnel.
- Hardness meters have a higher initial cost but are cost-effective in the long run due to their ease of use and quick readings. However, they require periodic calibration and sensor replacement.
For industries that require frequent testing, a hardness meter is a more practical option, whereas laboratories that prioritize accuracy may find EDTA titration more economical.
Where Are These Methods Used?
Different industries and applications require different hardness testing methods. Here’s where each method is commonly used:
- EDTA Titration is used in:
- Research laboratories
- Pharmaceutical industries
- Food and beverage testing
- Environmental monitoring
- Hardness Meters are used in:
- Water treatment plants
- Industrial cooling systems
- Residential water quality testing
- Pool and spa maintenance
Pros and Cons of EDTA Titration and Hardness Meters
Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages. Let’s look at them in detail.
Pros and Cons of EDTA Titration

✅ Pros:
- Highly accurate and reliable
- Detects low concentrations precisely
- Cost-effective for laboratory use
❌ Cons:
- Time-consuming process
- Requires trained personnel
- Prone to human errors if not performed correctly
Pros and Cons of Hardness Meters
✅ Pros:
- Quick and easy to use
- Portable for field testing
- No need for chemical reagents
❌ Cons:
- May give inaccurate results due to calibration issues
- Affected by temperature and electrical interference
- Higher initial investment cost
Which One Should You Choose?
The choice between EDTA titration and a hardness meter depends on your needs.
- If you need high accuracy for research or laboratory settings, EDTA titration is the better choice.
- If you need quick, on-the-go testing with minimal effort, a hardness meter is the ideal solution.
- For industrial applications requiring frequent measurements, a hardness meter is more practical.
- For precise chemical analysis in regulated environments, EDTA titration is recommended.
Thoughts on EDTA Titration vs. Hardness Meter
Both EDTA titration and hardness meters have their place in water hardness measurement. If precision and detailed analysis are required, EDTA titration is the best method. However, if you need quick, on-site readings, a hardness meter is more convenient.
Ultimately, the best method depends on your specific requirements, budget, and the level of accuracy needed. Some industries even use both methods—hardness meters for quick testing and EDTA titration for confirmation and calibration.
The Bottom Line
So, is EDTA titration more accurate than a hardness meter? Yes, EDTA titration generally provides more accurate results due to its ability to precisely measure calcium and magnesium concentrations. However, it requires more time, effort, and expertise. Hardness meters, on the other hand, offer quick and easy measurements but may be less reliable due to external interferences.
For high-precision applications, EDTA titration is the best choice. For quick field testing and industrial use, a hardness meter is more practical. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each method will help you make an informed decision based on your needs.