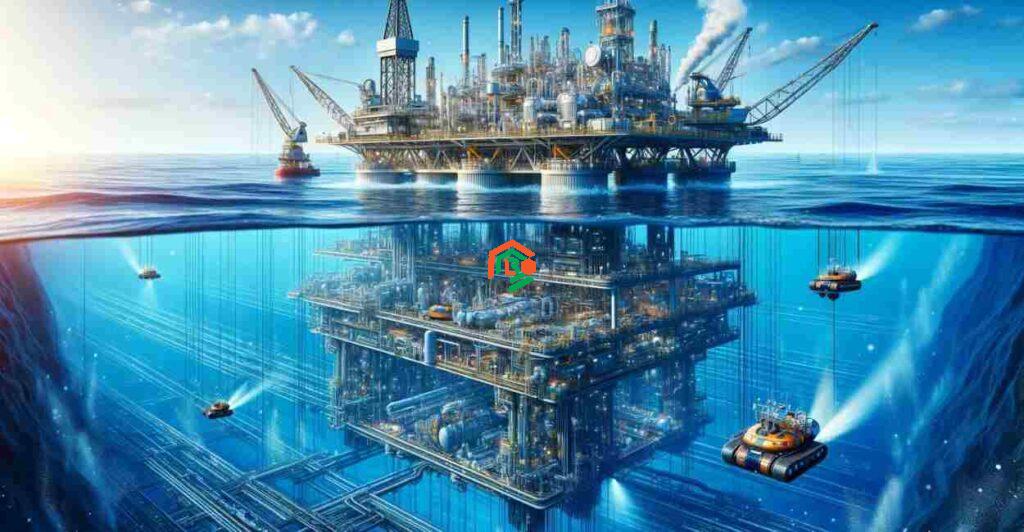
Oil is one of the most important resources in the world. It powers our cars, heats our homes, and helps make thousands of everyday products. But much of the easy-to-reach oil on land has already been found and used. So, where does the rest of it come from? One answer lies deep under the ocean. This is where deep offshore technology comes in. This technology helps us find, drill, and extract oil from under the sea, sometimes at depths of more than 3,000 meters (10,000 feet)! But how does it work? And how do we protect the ocean while drilling for oil? Let’s find out.
What Is Deep Offshore Technology?
Deep offshore technology is the set of tools, machines, and techniques used to drill for oil far out in the ocean, in waters deeper than 500 meters (1,640 feet). Unlike oil drilling on land or in shallow waters, deep offshore drilling is much more complex. The deeper the water, the more challenging it is to reach and extract oil safely.
This technology includes massive oil platforms, strong pipes, advanced robots, and high-tech monitoring systems that allow oil companies to operate miles away from the shore. Without these innovations, it would be impossible to get oil from the deep ocean.
Why Do We Need Deep Offshore Technology?
The world still relies on oil for energy, transportation, and manufacturing. However, oil reserves on land and in shallow waters are running low. To meet global demand, companies have turned to deep-sea drilling to access oil hidden beneath the ocean floor.
Deep offshore drilling provides access to huge amounts of oil that would otherwise be unreachable. Some of the world’s largest oil fields are located far out at sea, and without deep offshore technology, we wouldn’t be able to extract these valuable resources.
Additionally, advancements in offshore drilling technology have made the process safer and more efficient, reducing the risk of oil spills and environmental damage.
How Do We Drill for Oil Under the Sea?
Drilling for oil in deep offshore waters is a complex process that requires advanced technology and engineering. The process involves several key steps:

- Finding Oil Under the Ocean
- Oil companies first use seismic surveys to locate potential oil reserves beneath the ocean floor. These surveys send sound waves into the ground and measure how they bounce back, helping scientists determine where oil is trapped.
- Building Oil Platforms
- Once a promising site is found, oil companies construct huge platforms that float on the water or are anchored to the ocean floor. These platforms hold the drilling equipment and house the workers.
- Drilling the Well
- Special drill bits are used to dig deep into the seabed, sometimes reaching depths of several kilometers. As the drill moves downward, special pipes and cement are used to keep the well stable.
- Extracting the Oil
- Once the oil is reached, special pipes and pumps are used to bring it up to the surface, where it is processed and transported to refineries.
Let’s take a closer look at some of the key components that make deep offshore drilling possible.
The Role of Big Oil Platforms
Oil platforms are like floating cities in the middle of the ocean. There are different types of platforms, including:
- Fixed Platforms – These are attached to the ocean floor and used in shallower waters.
- Floating Platforms – These include semi-submersible rigs and drillships that float on the water’s surface but are stabilized using anchors or dynamic positioning systems.
- Tension-Leg Platforms – These are anchored to the seabed using long, flexible cables.
These platforms hold all the drilling equipment, storage tanks, and living quarters for workers. Some even have helicopter landing pads and recreation areas.
Special Pipes That Bring Oil Up
Extracting oil from the ocean floor requires special pipes called riser systems. These pipes must be strong enough to handle high pressure and extreme temperatures while also preventing leaks. Some common types include:
- Flexible Risers – These move with ocean currents without breaking.
- Steel Catenary Risers (SCRs) – These are rigid pipes that can transport oil over long distances.
- Top-Tensioned Risers – These stay straight and stable even in rough seas.
Without these advanced pipes, oil couldn’t travel from the seabed to the surface safely.
Robots That Help Underwater
Deep-sea drilling requires the help of robots, also known as remotely operated vehicles (ROVs). These robots:
- Inspect and repair equipment on the seabed
- Monitor drilling operations
- Help prevent oil spills by detecting leaks early
Since human divers can’t go deep enough to work on underwater oil rigs, these robots play a crucial role in offshore drilling.
How Do We Keep the Ocean Safe?
Drilling for oil in the ocean can be risky, but modern technology has made it safer. Companies use several methods to protect the environment:
- Blowout Preventers (BOPs) – These devices stop oil from escaping if there is a sudden pressure change.
- Double-Layered Pipelines – Extra layers help prevent leaks.
- Oil Spill Response Plans – Teams are always on standby to contain and clean up spills if they happen.
- Environmental Monitoring – Scientists track water quality and marine life to ensure drilling activities don’t cause major harm.
While deep-sea drilling is not risk-free, these safety measures help reduce the impact on the ocean.
What Are the Biggest Deep Offshore Oil Fields?
Some of the largest deep offshore oil fields in the world include:
- Gulf of Mexico (USA) – Home to massive oil fields like Thunder Horse and Atlantis.
- Brazil’s Pre-Salt Fields – One of the richest offshore oil regions in the world.
- North Sea (UK & Norway) – Produces significant amounts of oil from deep waters.
- West Africa (Nigeria & Angola) – Contains large deepwater oil reserves.
These regions contribute a major portion of the world’s oil supply.
The Future of Deep Offshore Technology
As technology improves, deep offshore drilling is becoming safer, more efficient, and more environmentally friendly.

Will We Always Need Oil?
While renewable energy is growing, oil is still a key resource. However, as electric cars and alternative fuels become more popular, the world may rely less on deep offshore drilling in the future.
Can Deep Offshore Technology Get Even Better?
Yes! Innovations like AI-powered monitoring systems, automated drilling rigs, and carbon capture technology are making offshore drilling more advanced. These technologies reduce costs, improve safety, and lower environmental impact.
How Do We Keep the Ocean Safe?
In the future, stricter regulations, better oil spill response systems, and eco-friendly drilling techniques will help protect the ocean even more. Some companies are even investing in green energy alongside offshore oil drilling.
The Bottom Line
Deep offshore technology allows us to extract oil from the ocean floor, supplying energy to millions of people worldwide. While this process is complex and challenging, modern innovations have made it safer and more efficient. However, as the world shifts toward renewable energy, deep offshore drilling may play a smaller role in the future.
For now, deep-sea oil exploration remains a crucial part of the global energy industry—but it must be done responsibly to protect our planet’s oceans.