African bulls are among the most fascinating animals on the planet. With their huge size, impressive horns, and unmatched strength, they stand out in the wild. Found across parts of Africa, these bulls are symbols of power, survival, and natural beauty. Let’s dive deep into the world of African bulls and uncover what makes them so special.
What Is an African Bull?
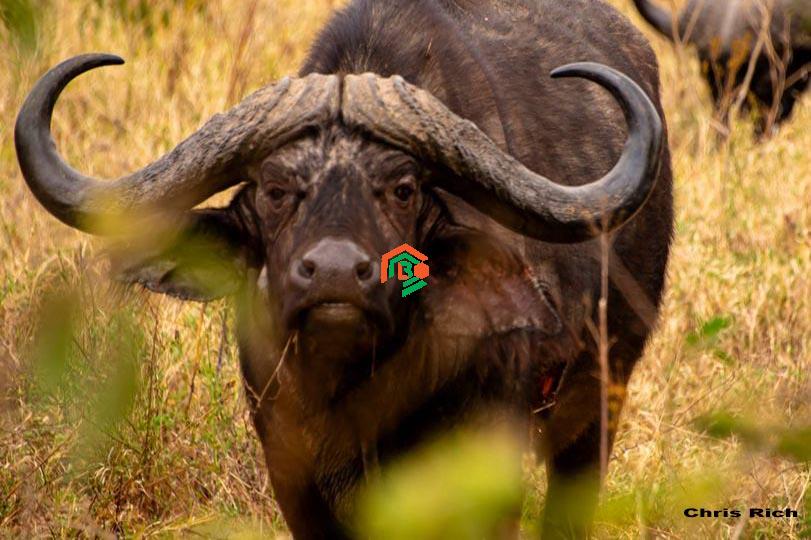
An African bull is the male version of certain wild cattle species found in Africa. The term can refer to several large mammals, but it most commonly relates to the African buffalo or Cape buffalo – a strong, horned animal native to sub-Saharan Africa. These bulls are not the same as domestic cows or bulls you might see on farms in the U.S. Instead, they are wild, powerful, and incredibly tough.
African bulls are known for their bulk and might. The males are usually much larger than the females and can weigh over 1,500 pounds. With sharp curved horns and muscular frames, they are built for survival in the wild. People often confuse African bulls with other African giants like elephants or rhinos, but they’re part of the wild cattle family.
They are not related to the American bison or the Indian water buffalo, even though they may look similar. These bulls are part of Africa’s famous “Big Five” animals, a group that includes lions, elephants, leopards, and rhinos. That’s how important and respected they are in the wild!
Where Do African Bulls Live?
African bulls mainly live in sub-Saharan Africa, especially in countries like Kenya, Tanzania, South Africa, Botswana, and Uganda. They prefer places with lots of grass, water, and space to roam. These bulls love the savannas, swamps, grasslands, and even forested areas, where they can find both food and protection from predators.
They are highly adaptable and can survive in both wet and dry climates. However, they tend to avoid deserts and deep jungles. Their favorite places are open spaces near rivers, lakes, or watering holes. African bulls rely heavily on water, so they stay close to places where they can drink daily. That’s one of the reasons you often see them around watering holes in African national parks.
What Do African Bulls Eat?
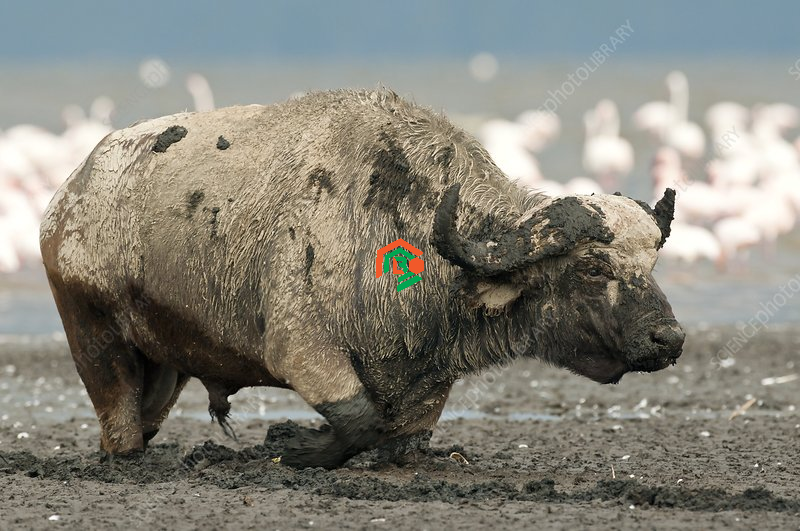
African bulls are herbivores, which means they only eat plants. Their diet mainly consists of grass, but they also eat leaves, shrubs, and other plants when needed. Because of their large size, they need to eat a lot to stay strong and healthy. They can graze for hours each day to get enough food.

Grass Is Their Favorite Food
African bulls love grass. It’s their number one food source. They prefer short, green grass that’s easy to chew and digest. In fact, most of their day is spent grazing, especially in the early morning or late afternoon when the weather is cooler.
They Love Water Too
Even though they don’t eat water, African bulls need it just as much as food. They drink water at least once a day. That’s why you’ll often find them near rivers, lakes, or watering holes. Without water, they can’t survive for long, especially in hot areas.
Chewing All Day Long
These bulls have a special way of eating called rumination. They chew their food, swallow it, then bring it back up to chew it again. This helps them break down tough plant material and get the most nutrition out of it. It’s like nature’s slow-cooking system for digestion!
Why Are African Bulls So Strong?
African bulls are known for their powerful muscles, thick necks, and heavy bodies. But what really makes them strong is their natural environment. They grow up in the wild, where they must be tough to survive predators like lions, crocodiles, and hyenas. Only the strongest bulls live long lives.
Their horns also play a big role in their strength. These curved, sharp tools are used for defense and for fighting other bulls during mating season. When two bulls fight, it’s a powerful sight – their horns crash together, and the stronger one usually wins the right to lead or mate.
Their strong bones, solid hooves, and thick skin also help protect them from injury. They’ve evolved over thousands of years to be strong and durable. Nature made them tough because life in the wild is not easy.
Are African Bulls Dangerous?
Yes, African bulls can be dangerous, especially if they feel threatened. They are not naturally aggressive toward humans, but they will defend themselves and their herd if they sense danger. Many wildlife experts rank them among the most dangerous animals in Africa, mainly because of their unpredictable behavior.
Unlike other animals that may run away, African bulls often stand their ground. If a predator or human gets too close, they may charge with full force. Their horns can cause serious injury or even death. That’s why safari guides always advise tourists to keep a safe distance.
They are especially dangerous when injured or separated from their herd. A lone bull, also called a “dagga boy,” is often older and more aggressive. These bulls have earned a reputation for being fearless and sometimes even reckless.
How Do African Bulls Protect Themselves?
In the wild, survival depends on being able to defend yourself. African bulls are masters at this. They use their size, strength, and herd behavior to stay safe.

Horns Like Weapons
One of their most important defense tools is their horns. These curved, hard horns are incredibly strong and sharp. Bulls use them to fight off predators like lions or to challenge other bulls. When they swing their heads, it’s like being hit with a baseball bat – only heavier.
The horns are also used to protect the younger bulls and cows in the herd. The big males will often take the lead in defending the group during a lion attack.
Moving in Herds
African bulls rarely travel alone. They live in large herds, sometimes with hundreds of other buffalo. This herd behavior is one of their greatest strengths. When a predator approaches, the bulls will form a circle around the young or weaker members. Together, they are much stronger than any single predator.
There have even been cases where a whole herd has turned on a pride of lions, chasing them away. It’s an amazing display of teamwork and strength.
How Big Can an African Bull Get?
African bulls are massive. A full-grown male can weigh between 1,300 and 2,000 pounds (about 600 to 900 kilograms). They can stand up to 5.6 feet tall at the shoulder and measure more than 10 feet long from nose to tail.
Their horns can be over 3 feet wide, especially in older bulls. Some bulls grow a horn structure called a “boss,” which is a thick shield in the center of their head where the horns meet. This boss can be as hard as concrete and is used during fights.
What Makes African Bulls Special?
African bulls are not just strong – they are also smart, social, and essential to the ecosystem. They play a key role in the food chain. By eating grass and plants, they help shape the land. They also provide food for predators like lions and crocodiles.
But beyond that, African bulls symbolize power, courage, and survival. Many African cultures respect these animals deeply and even feature them in stories and artwork. In modern wildlife conservation, they are a key species that helps scientists understand the health of ecosystems.
They are also amazing to watch. Seeing a herd of bulls moving across the savanna is like watching nature’s army – strong, united, and unstoppable.
The Bottom Line
African bulls are some of the strongest and most fascinating animals in the world. They live in the wild lands of Africa, where they face danger every day and survive thanks to their strength, intelligence, and group unity. These bulls eat grass, love water, and spend most of their time chewing and grazing. But when it comes to danger, they are ready to fight with sharp horns and massive bodies.
They may look similar to domestic bulls, but African bulls are wild at heart. They are protectors of their herds, fighters in the wild, and a symbol of natural strength. Whether you’re a young animal lover or a wildlife explorer, African bulls are a creature worth learning about.