The Maynard Operation Sequence Technique (MOST) is a work measurement system designed to help businesses save time and improve efficiency. It’s a method used to analyze tasks, break them down into steps, and assign standard times to each activity. This makes it easier for companies to plan, control, and optimize their operations. In this guide, we’ll explain everything about MOST in a simple way, so anyone—even a 10-year-old—can understand it.
What Is the Maynard Operation Sequence Technique?
The Maynard Operation Sequence Technique, commonly known as MOST, is a system for measuring the time it takes to perform work. Developed in the 1960s by H.B. Maynard and Company, it was designed as a faster alternative to traditional time studies and methods like Methods-Time Measurement (MTM). MOST simplifies the process of work measurement by using standard sequences and time values for basic movements.
In simple words, MOST is like having a universal timer for common work actions. Instead of measuring every small detail separately, it groups actions into patterns and gives each pattern a time value. This saves time for industrial engineers and helps companies achieve higher productivity without sacrificing quality.
Why Do Companies Use It?
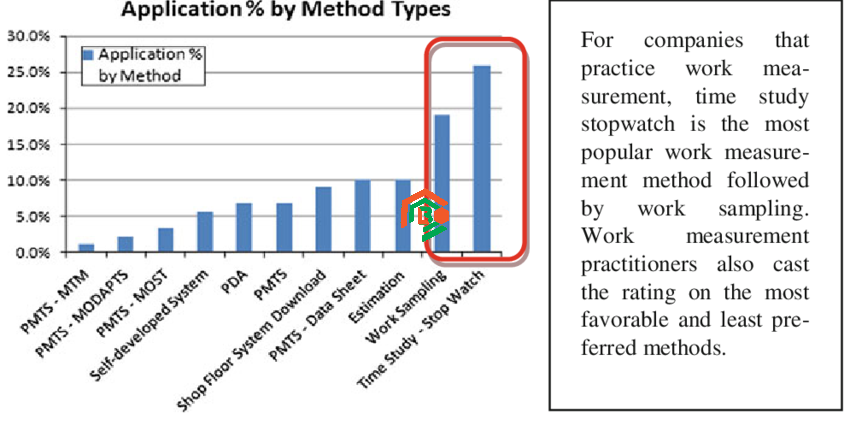
Companies use the Maynard Operation Sequence Technique because it’s practical, accurate, and much quicker than older methods. Measuring how long tasks take in a factory or office used to involve timing every movement with a stopwatch. That process was slow and sometimes gave inconsistent results.
MOST changed the game by giving organizations a reliable system for setting standard times without the hassle of extensive observation. With it, companies can identify wasted effort, balance workloads, and make better decisions about staffing and production rates. It’s popular in industries where even small time savings can translate into huge cost reductions.
How Does Maynard Operation Sequence Technique Work?
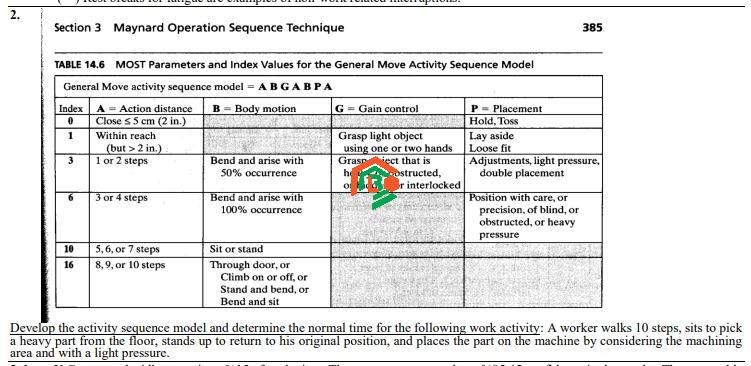
MOST works by analyzing jobs as a sequence of basic steps and assigning time values to those steps. The technique is based on the idea that all work involves a predictable series of motions like reaching, moving, grasping, positioning, and releasing. Instead of timing each motion, MOST uses pre-determined time units for these motion patterns.

This makes the process quicker, more consistent, and easier to apply in real-world settings. Let’s break it down further:
Breaking Down Jobs into Steps
The first step in using MOST is breaking down a job into smaller, logical steps. For example, if a worker assembles a part, the steps might include picking up a tool, moving it into position, fastening a bolt, and putting the tool back. Each of these steps fits into a standard sequence defined in the MOST system.
By mapping out these sequences, engineers can understand the flow of work and pinpoint where delays or inefficiencies happen.
Using Pre-Set Time Patterns
MOST includes pre-set time values for common sequences of movements. These are called BasicMOST, MiniMOST, and MaxiMOST, depending on the complexity of the task.
- BasicMOST is used for medium-level activities like assembling components.
- MiniMOST is used for very detailed, short-duration tasks like electronics assembly.
- MaxiMOST is ideal for large-scale, longer-duration activities like material handling.
These patterns are applied instead of manually timing every action, which saves time and reduces human error.
Calculating Total Time Easily
Once all steps are assigned their time values, they’re added together to find the total time for the entire job. This total time becomes a standard for how long the job should take when performed correctly.
This standard helps managers set realistic expectations for workers and monitor productivity without constant supervision.
Benefits of Maynard Operation Sequence Technique
The Maynard Operation Sequence Technique offers many benefits to organizations of all sizes. One of its biggest strengths is speed. It’s estimated to be about 10 times faster than traditional time study methods, which means companies can implement it without investing excessive time or resources.
It also delivers consistent results because it relies on standardized motion patterns. This reduces variations caused by different observers or external factors. Additionally, MOST is flexible enough to be applied in manufacturing, logistics, service industries, and even healthcare.
By using MOST, companies can:
- Improve productivity by identifying and eliminating wasted motion
- Standardize work methods for better quality control
- Plan labor requirements more accurately
- Enhance worker safety by optimizing ergonomics
- Support lean manufacturing and continuous improvement initiatives
Where Is Maynard Operation Sequence Technique Used?
MOST is used in a wide variety of industries where measuring and improving human work is critical. It’s especially popular in manufacturing environments, but its applications go far beyond the factory floor.
Factories and Assembly Lines
In factories and assembly lines, MOST is used to design efficient workflows. It helps in determining the best way to assemble products, reduces bottlenecks, and ensures that all workers are performing tasks in the most effective way possible.
Engineers can redesign workstation layouts or adjust line balancing based on MOST analysis. For example, in an automotive plant, MOST can set standards for how long it should take to install a car door or mount a wheel.
Service Industries
MOST isn’t limited to manufacturing. Service industries like logistics, healthcare, and retail also use it. For example, in a hospital, MOST can help plan how long nurses spend on patient care activities. In warehouses, it’s used to set time standards for picking, packing, and shipping operations.
Challenges of Using MOST
Like any system, MOST has its challenges. One issue is the need for training. Engineers and supervisors must learn how to analyze tasks and apply MOST correctly. Another challenge is resistance from workers who might feel that time standards are too strict.
To overcome these challenges, companies need to involve employees in the process and ensure that standards are fair and achievable.
How to Learn Maynard Operation Sequence Technique?
Learning MOST usually involves formal training from certified organizations. Many industrial engineers take courses that teach the basics of task analysis, motion patterns, and applying time standards. Some universities also include MOST in their industrial engineering programs.
For professionals, certification in MOST can open doors to careers in work measurement, productivity consulting, and process improvement.
What Is Maynard Operation Sequence Technique?
To sum it up again, the Maynard Operation Sequence Technique is a work measurement tool that simplifies task analysis using pre-determined motion patterns and time values. It helps companies save time, improve productivity, and maintain consistent quality. Whether in factories, warehouses, or offices, MOST makes it easier to plan and control human work effectively.
The Bottom Line
The Maynard Operation Sequence Technique is a powerful tool for organizations aiming to get more done in less time. By breaking down work into logical steps and applying pre-set time standards, it helps businesses operate smarter, not harder.
MOST is more than just a time measurement method—it’s a pathway to higher efficiency, better ergonomics, and continuous improvement. For companies in the United States and worldwide, understanding and applying MOST can lead to significant competitive advantages in today’s fast-paced markets.