Introduction
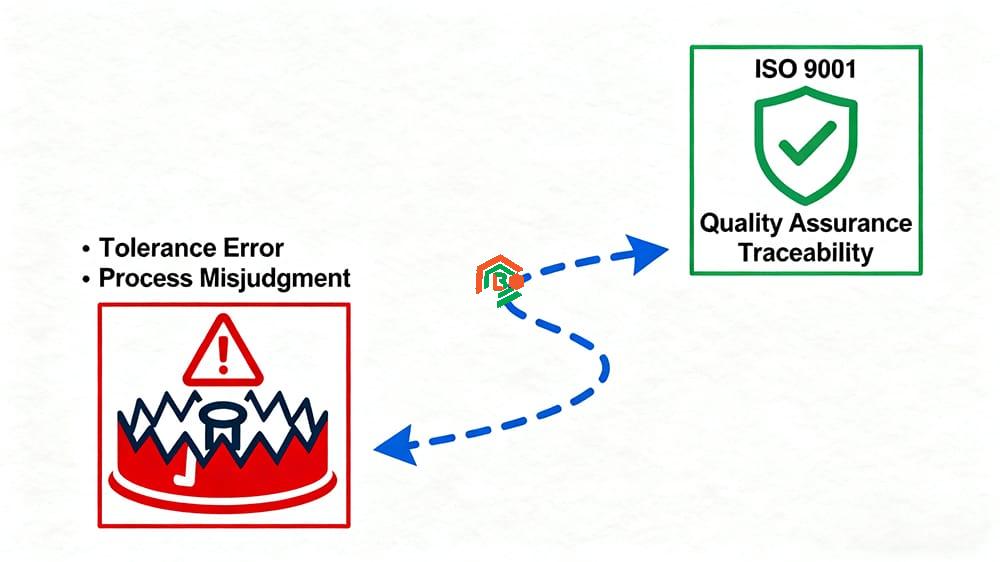
According to ISO surveys, over 30% of manufacturing projects are delayed due to neglect of design-for-manufacturability principles. In one real-world case, a supplier failed to specify critical tolerances in technical drawings, resulting in a scrap rate of 20%. This not only caused financial losses in the hundreds of thousands but also delayed customer delivery schedules.
These scenarios highlight the three quality pitfalls that ISO 9001 certified manufacturers are trained to avoid. By understanding these risks – tolerance control, process misjudgment, and supplier reliability—engineers, procurement managers, and manufacturing business owners can significantly reduce project failures and ensure smoother production outcomes.
Pitfall 1: Why is tolerance control in CNC machining so critical?
Common Issues
Many manufacturing failures originate from ignoring tolerance considerations during the design stage.
Root Cause
According to Design for manufacturability, integrating tolerance requirements early in product design is essential to ensure parts can be consistently produced and assembled. Neglecting DFM principles often results in components that fail to fit or function properly, leading to costly rework.
Case Study Table: Tolerance Control in Practice
| Scenario | Tolerance Approach | Outcome |
| Automotive bracket design | Loose tolerance ±0.5 mm | 15% parts rejected due to misalignment |
| Medical device housing | Tight tolerance ±0.05 mm with DFM review | Scrap rate reduced by 20%, assembly success improved |
| Aerospace fastener | GD&T applied under DFM framework | Zero defects in pilot batch, improved reliability |
Solution
Industry cases show that manufacturers who embed tolerance analysis into their DFM workflow reduce scrap rates by up to 20%. Applying geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) disciplines within a DFM framework helps engineers translate functional requirements into manufacturable specifications.
Benefit
Early tolerance control reduces waste, improves reliability, and ensures smoother downstream production – an essential practice in Precision Engineering.
Pitfall 2: How to choose the right CNC process to avoid cost traps?
Common Issues
Companies often misjudge between turning and milling, leading to higher costs.
Root Cause
Different processes suit different geometries. Complex surfaces are better suited for 5-axis milling, while simple cylindrical parts are ideal for turning.
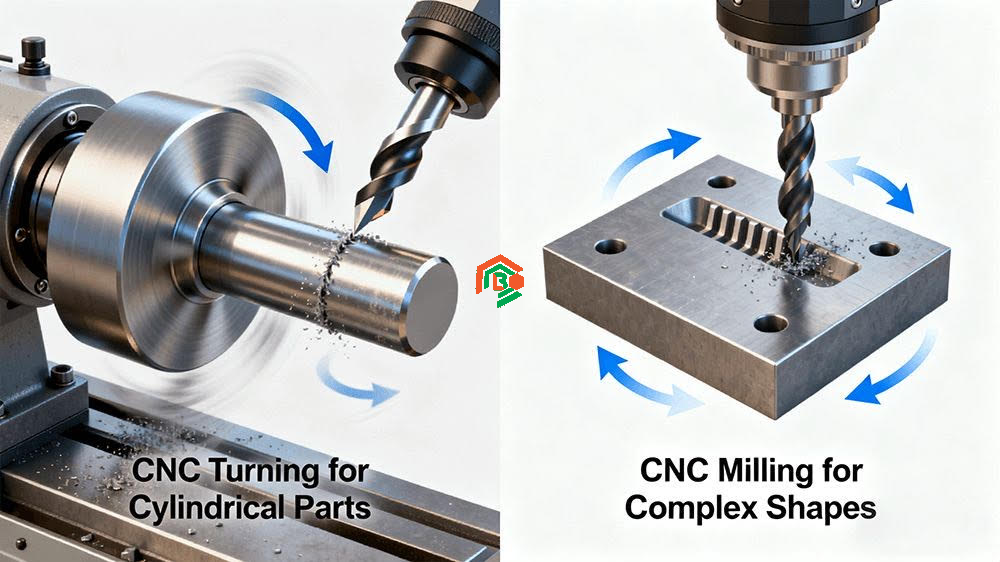
Fig. 2: Misjudging processes is a common cost trap. Turning is ideal for rotational parts, while milling handles complex contours – correct selection can reduce machining time by 30%.
Solution
Understanding process differences is key to cost optimization. A detailed industry guide (3-Axis vs 5-Axis CNC Machining guide) explains how to select the best process, referencing DFM principles to highlight the importance of tolerance control.
Benefit
Correct process selection can reduce machining time by 30% and lower overall costs.
Pitfall 3: How does supplier certification reduce quality risks?
Common Issues
Procurement managers often face delays when choosing non-certified suppliers.S
Root Cause
Non-certified manufacturers lack process traceability, increasing the risk of batch defects.
Solution
According to ISO 9001:2015 standards, a robust quality management system requires process traceability, which can reduce project risks by up to 40%.
Benefit
Certified suppliers provide higher reliability and lower rework rates.
Extended Risk: What role does rapid prototyping play in manufacturing decisions?
Skipping prototype validation often amplifies design flaws in mass production. Industry data shows that companies using rapid prototyping can detect up to 80% of potential issues before mass production. This saves modification costs and shortens time-to-market.
Extended Risk: How to avoid hidden risks in cross-process selection?
Switching between CNC, sheet metal, and injection molding often overlooks material-process compatibility. For example, titanium alloys are better suited for 5-axis machining, while plastic parts are more suitable for injection molding. Developing a cross-process comparison chart clarifies optimal material-process matches, avoiding scrap and extra costs.
FAQs
1. What are the most common mistakes in CNC machining? → Ignoring tolerance control and misjudging process selection.
2. What is the significance of ISO certification for manufacturers? → It ensures process traceability and reduces risks.
3. How to decide between turning and milling? → Based on part geometry and complexity.
4. Does rapid prototyping really save costs? → Yes, it identifies most issues before mass production.
5. What should be considered in cross-process selection? → Material properties and process compatibility.
Author Bio
This article is authored by LS Manufacturing, an ISO 9001, IATF 16949, ISO 13485, AS9100D certified manufacturer. Which helps clients overcome challenges in CNC machining, injection molding, sheet metal fabrication, and rapid prototyping. Learn more about our CNC Machining Services.